
👇 🔠 🔤 👇


🏛 Why W is called "double U"
🇫🇷 Why do the French call Y a "Greek I"?
💤 Is it ZEE or ZED??
✏️ How I and J were the same for the Romans
🤔 Why we can easily confuse U and V



00:00 Introduction
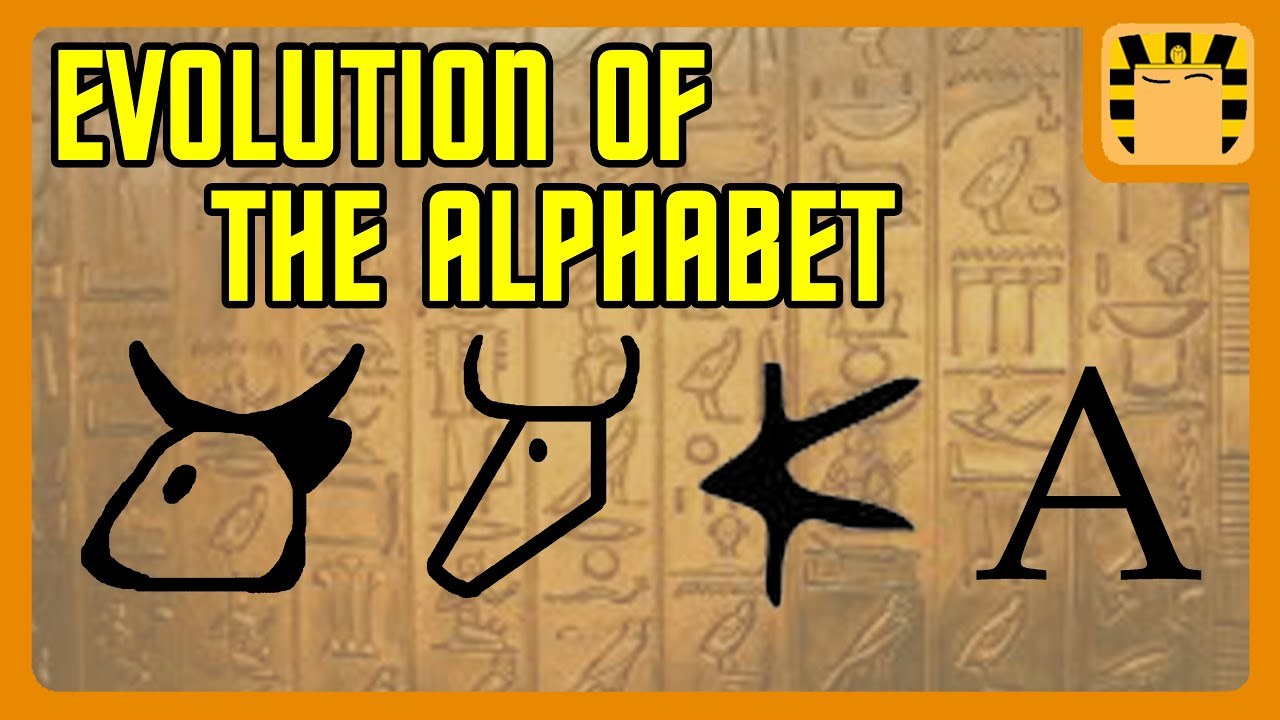
00:43 The birth of the alphabet
01:25 Hieroglyphics: A & B
04:13 C, E, K, M, N, O & R
06:04 L, S, D & Q - Early Semitic
09:23 F, U, V & Y - Ypsilon
10:35 W - double U
11:34 I & J - Latin double
13:08 G, H, P, T & X
14:29 Z - zed or zee?

A is for Ox by Lyn Davies: https://www.goodreads.com/en/book/sho...
(Thanks to those who suggested I read it)
Weird plurals in English: https://youtu.be/3rhxeDInKu8
Lost letters of the alphabet: https://youtu.be/wJxKyh9e5_A

Peter T. Daniels distinguishes an abugida, a set of graphemes that represent consonantal base letters that diacritics modify to represent vowels, like in Devanagari and other South Asian scripts, an abjad, in which letters predominantly or exclusively represent consonants such as the original Phoenician, Hebrew or Arabic, and an alphabet, a set of graphemes that represent both consonants and vowels. In this narrow sense of the word, the first true alphabet was the Greek alphabet, which was based on the earlier Phoenician abjad.
Of the dozens of alphabets in use today, the most popular is the Latin alphabet, which is most commonly used in Europe and North America. Although, it has influence and use worldwide. Languages often use extra letters or diacritical marks to make up for differences. The alphabet was originally derived from an archaic version of the Greek alphabet, called Euboean, which was used in the Greek colonies in Italy. The influence of which spread to other alphabets such as Latin, but also Etruscan as well.
Alphabets are usually associated with a standard ordering of letters. This makes them useful for purposes of collation, which allows words to be sorted in a specific order, commonly known as the alphabetical order. It also means that their letters can be used as an alternative method of "numbering" ordered items; in such contexts as numbered lists and number placements.
There are also names for letters in some languages. This is known as acrophony; It's present in some modern scripts, such as Greek, and many Semitic scripts, such as; Arabic, Hebrew, and Syriac. It was used in some ancient alphabets, such as in Phoenician. However, this system is not present in all languages, such as the Latin alphabet, which adds a vowel after a character for each letter. Some systems also used to have this system but later on abandoned it for a system similar to Latin, such as Cyrillic.

.gif)
No comments:
Post a Comment