Requiem Mass
Mass for the Dead
Latin: Missa pro defunctis
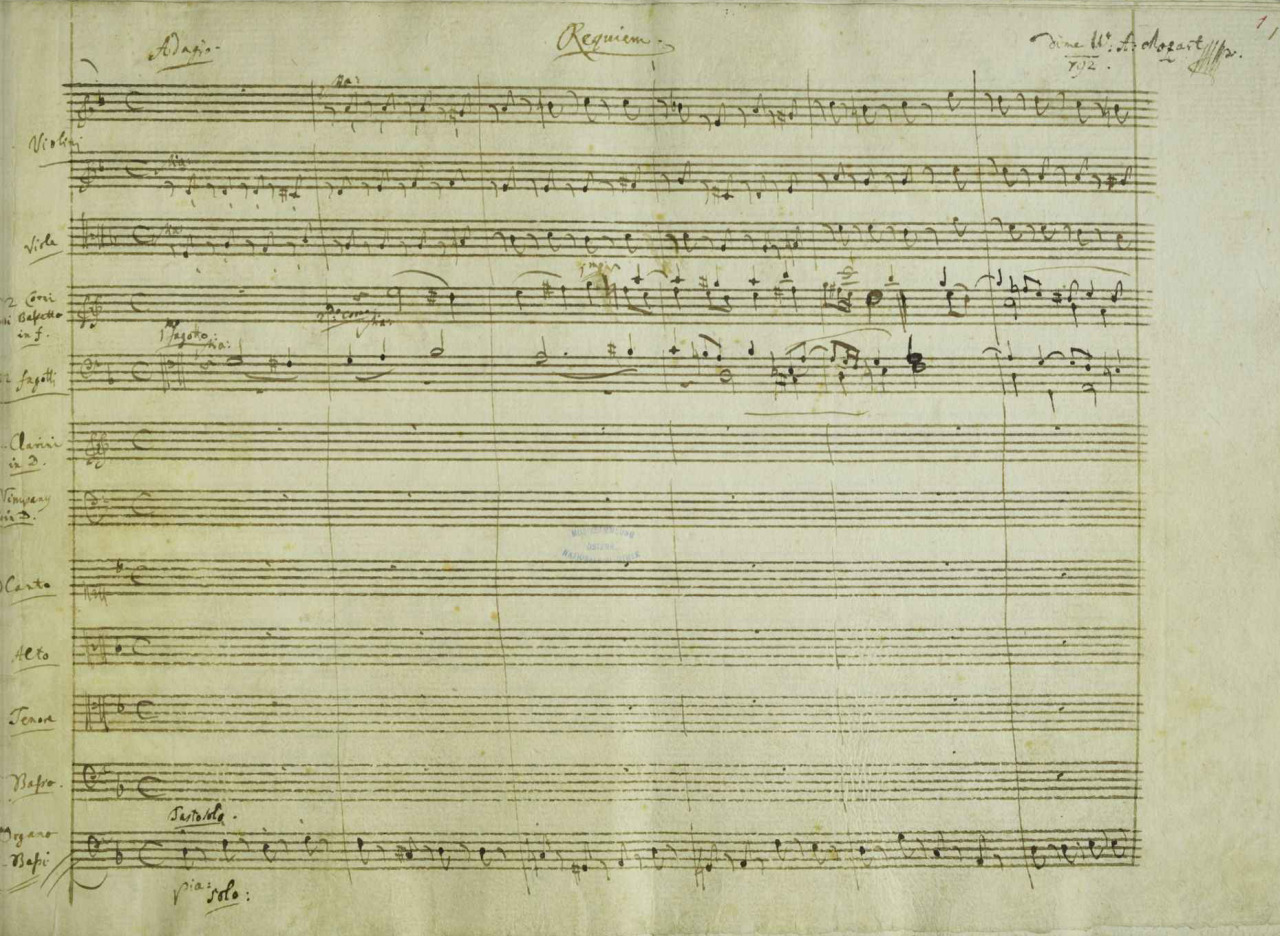

A portion of the manuscript of Mozart's Requiem, K 626 (1791), showing his heading for the first movement.
Mass for the Dead
Latin: Missa pro defunctis

A portion of the manuscript of Mozart's Requiem, K 626 (1791), showing his heading for the first movement.
A Requiem or Requiem Mass, also known as Mass for the dead (Latin: Missa pro defunctis) or Mass of the dead (Latin: Missa defunctorum), is a Mass in the Catholic Church offered for the repose of the soul or souls of one or more deceased persons, using a particular form of the Roman Missal. It is frequently, but not necessarily, celebrated in the context of a funeral.
Musical settings of the propers of the Requiem Mass are also called Requiems, and the term has subsequently been applied to other musical compositions associated with death and mourning, even when they lack religious or liturgical relevance.
The term is also used for similar ceremonies outside the Roman Catholic Church, especially in the Anglo-Catholic branch of Anglicanism and in certain Lutheran churches. A comparable service, with a wholly different ritual form and texts, exists in the Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic Churches, as well as in the Methodist Church.
The Mass and its settings draw their name from the introit of the liturgy, which begins with the words "Requiem aeternam dona eis, Domine" – "Grant them eternal rest, O Lord". ("Requiem" is the accusative singular form of the Latin noun requies, "rest, repose".) The Roman Missal as revised in 1970 employs this phrase as the first entrance antiphon among the formulas for Masses for the dead, and it remains in use to this day.
Liturgical rite
In earlier forms of the Roman Rite, some of which are still in use, a Requiem Mass differs in several ways from the usual Mass in that form. Some parts that were of relatively recent origin, including some that have been excluded in the 1970 revision, are omitted. Examples are the psalm Iudica at the start of Mass, the prayer said by the priest before reading the Gospel (or the blessing of the deacon, if a deacon reads it), and the first of the two prayers of the priest for himself before receiving Communion. Other omissions include the use of incense at the Introit and the Gospel, the kiss of peace, lit candles held by acolytes when a deacon chants the Gospel, and blessings. There is no Gloria in excelsis Deo and no recitation of the Creed; the Alleluia chant before the Gospel is replaced by a Tract, as in Lent; and the Agnus Dei is altered. Ite missa est is replaced with Requiescant in pace (May they rest in peace); the "Deo gratias" response is replaced with "Amen". Black is the obligatory liturgical colour of the vestments in the earlier forms, while the later form allows a choice between black and violet, and in some countries, such as England and Wales, white. The sequence Dies Iræ, recited or sung between the Tract and the Gospel, is an obligatory part of the Requiem Mass in the earlier forms. As its opening words, Dies irae (Day of wrath), indicate, this poetic composition speaks of the Day of Judgment in fearsome terms; it then appeals to Jesus for mercy.
Musical settings of the propers of the Requiem Mass are also called Requiems, and the term has subsequently been applied to other musical compositions associated with death and mourning, even when they lack religious or liturgical relevance.
The term is also used for similar ceremonies outside the Roman Catholic Church, especially in the Anglo-Catholic branch of Anglicanism and in certain Lutheran churches. A comparable service, with a wholly different ritual form and texts, exists in the Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic Churches, as well as in the Methodist Church.
The Mass and its settings draw their name from the introit of the liturgy, which begins with the words "Requiem aeternam dona eis, Domine" – "Grant them eternal rest, O Lord". ("Requiem" is the accusative singular form of the Latin noun requies, "rest, repose".) The Roman Missal as revised in 1970 employs this phrase as the first entrance antiphon among the formulas for Masses for the dead, and it remains in use to this day.
Liturgical rite
In earlier forms of the Roman Rite, some of which are still in use, a Requiem Mass differs in several ways from the usual Mass in that form. Some parts that were of relatively recent origin, including some that have been excluded in the 1970 revision, are omitted. Examples are the psalm Iudica at the start of Mass, the prayer said by the priest before reading the Gospel (or the blessing of the deacon, if a deacon reads it), and the first of the two prayers of the priest for himself before receiving Communion. Other omissions include the use of incense at the Introit and the Gospel, the kiss of peace, lit candles held by acolytes when a deacon chants the Gospel, and blessings. There is no Gloria in excelsis Deo and no recitation of the Creed; the Alleluia chant before the Gospel is replaced by a Tract, as in Lent; and the Agnus Dei is altered. Ite missa est is replaced with Requiescant in pace (May they rest in peace); the "Deo gratias" response is replaced with "Amen". Black is the obligatory liturgical colour of the vestments in the earlier forms, while the later form allows a choice between black and violet, and in some countries, such as England and Wales, white. The sequence Dies Iræ, recited or sung between the Tract and the Gospel, is an obligatory part of the Requiem Mass in the earlier forms. As its opening words, Dies irae (Day of wrath), indicate, this poetic composition speaks of the Day of Judgment in fearsome terms; it then appeals to Jesus for mercy.
Mozart 😪 Requiem in D minor
(Complete/Full)
(Complete/Full)
👇 🎼 👇
 🎼
🎼
Requiem on You Tube
https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=requiem&lclk=hd&filters=hd
🎼
https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=Requiem+




Post Vatican II
In the liturgical reforms of the mid-20th century in the Roman Catholic Church following the Second Vatican Council, there was a significant shift in the funeral rites used by the Church. The emphasis on sorrow and grief was to be replaced by one which also includes the whole community's worship of God and in which the deceased is entrusted to God's love, based on trust in the salvific value of the Passion, Death and Resurrection of Jesus Christ.
The term "Requiem Mass" was often replaced by the term Mass of the Resurrection or Mass of Christian Burial, although the former was never official terminology. In line with this shift, the use of black vestments was made optional (and had mostly disappeared by the late 20th century, at least in the United States, although their use is seeing a resurgence), with the preference of many being for white, the color of joy associated with Easter, or purple, for a muted version of mourning. The texts used for the service made a similar change, with the overall theme of the service to be a proclamation of the promise of eternal life made by Jesus.
 Annual requiems
Annual requiems
A Solemn Requiem Mass is held by the Catholic Police Guild in October every year. It is celebrated in Westminster Cathedral, London to commemorate:
Requiem in other rites and churches
Requiem is also used to describe any sacred composition that sets to music religious texts which would be appropriate at a funeral, or to describe such compositions for liturgies other than the Roman Catholic Mass. Among the earliest examples of this type are the German settings composed in the 17th century by Heinrich Schütz and Michael Praetorius, whose works are Lutheran adaptations of the Roman Catholic requiem, and which provided inspiration for the mighty German Requiem by Brahms.
Such works include:
 Eastern Christian rites
Eastern Christian rites
Because of their great length, a full Requiem is rarely served. However, at least in the Russian liturgical tradition, a Requiem will often be served on the eve before the Glorification (canonization) of a saint, in a special service known as the "Last Panikhida."

Anglicanism
The Anglican Book of Common Prayer contains no Requiem Mass, but instead a service named "The Order for the Burial of the Dead". Within this service are several texts with rubrics stating that they shall be said or sung by the priest or clerks. The first few of these texts are found at the beginning of the service, while the rest are meant to occur during the actual burial of the body into the grave. These texts are typically dividing into seven, and collectively known as "funeral sentences". Composers who have set the Anglican burial service to music include William Croft, Thomas Morley, Thomas Tomkins, Orlando Gibbons, and Henry Purcell. The text of these seven sentences, from the 1662 Book of Common Prayer, is as follows:
 Music
Music
Many of the texts in the Requiem Mass have been set to music, including:
 History of musical compositions
History of musical compositions
For many centuries the texts of the requiem were sung to Gregorian melodies. The Requiem by Johannes Ockeghem, written sometime in the later half of the 15th century, is the earliest surviving polyphonic setting. There was a setting by the elder composer Dufay, possibly earlier, which is now lost: Ockeghem's may have been modelled on it. Many early compositions reflect the varied texts that were in use in different liturgies around Europe before the Council of Trent standardised texts used in liturgies. The requiem of Brumel, circa 1500, is the first to include the Dies Iræ. In the early polyphonic settings of the Requiem, there is considerable textural contrast within the compositions themselves: simple chordal or fauxbourdon-like passages are contrasted with other sections of contrapuntal complexity, such as in the Offertory of Ockeghem's Requiem.
In the 16th century, more and more composers set the Requiem mass. In contrast to practice in setting the Mass Ordinary, many of these settings used a cantus-firmus technique, something which had become quite archaic by mid-century. In addition, these settings used less textural contrast than the early settings by Ockeghem and Brumel, although the vocal scoring was often richer, for example in the six-voice Requiem by Jean Richafort which he wrote for the death of Josquin des Prez. Other composers before 1550 include Pedro de Escobar, Antoine de Févin, Cristóbal Morales, and Pierre de La Rue; that by La Rue is probably the second oldest, after Ockeghem's.
Over 2,000 Requiem compositions have been composed to the present day. Typically the Renaissance settings, especially those not written on the Iberian Peninsula, may be performed a cappella (i.e. without necessary accompanying instrumental parts), whereas beginning around 1600 composers more often preferred to use instruments to accompany a choir, and also include vocal soloists. There is great variation between compositions in how much of liturgical text is set to music.
Most composers omit sections of the liturgical prescription, most frequently the Gradual and the Tract. Fauré omits the Dies iræ, while the very same text had often been set by French composers in previous centuries as a stand-alone work.
Sometimes composers divide an item of the liturgical text into two or more movements; because of the length of its text, the Dies iræ is the most frequently divided section of the text (as with Mozart, for instance). The Introit and Kyrie, being immediately adjacent in the actual Roman Catholic liturgy, are often composed as one movement.
Musico-thematic relationships among movements within a Requiem can be found as well.
 Requiem in concert
Requiem in concert
Beginning in the 18th century and continuing through the 19th, many composers wrote what are effectively concert works, which by virtue of employing forces too large, or lasting such a considerable duration, prevent them being readily used in an ordinary funeral service; the requiems of Gossec, Berlioz, Verdi, and Dvořák are essentially dramatic concert oratorios. A counter-reaction to this tendency came from the Cecilian movement, which recommended restrained accompaniment for liturgical music, and frowned upon the use of operatic vocal soloists.
Notable compositions
Many composers have composed Requiems. Some of the most notable include the following (in chronological order):
 Modern treatments
Modern treatments
In the 20th century the requiem evolved in several new directions. The genre of War Requiem is perhaps the most notable, which comprise compositions dedicated to the memory of people killed in wartime. These often include extra-liturgical poems of a pacifist or non-liturgical nature; for example, the War Requiem of Benjamin Britten juxtaposes the Latin text with the poetry of Wilfred Owen, Krzysztof Penderecki's Polish Requiem includes a traditional Polish hymn within the sequence, and Robert Steadman's Mass in Black intersperses environmental poetry and prophecies of Nostradamus. Holocaust Requiem may be regarded as a specific subset of this type. The Requiem Ebraico (Hebrew Requiem) (1945) by Austrian-American composer Eric Zeisl, a setting of Psalm 92 dedicated to the memory of the composer's father "and the other countless victims of the Jewish tragedy in Europe," is considered the first major work of Holocaust commemoration. John Foulds's A World Requiem was written in the aftermath of the First World War and initiated the Royal British Legion's annual festival of remembrance. Recent requiem works by Taiwanese composers Tyzen Hsiao and Ko Fan-long follow in this tradition, honouring victims of the 228 Incident and subsequent White Terror. Other recent requiems include "Ossetian Requiem" (2006), in memory of the victims of the Beslan tragedy, by Ivan Moody, the "Requiem In D-Minor" (2009) composed by Allan Loucks, and the Requiem by Man-Ching Donald Yu, in remembrance of the victims of the 2008 Sichuan earthquake.
Lastly, the 20th century saw the development of the secular Requiem, written for public performance without specific religious observance, such as Frederick Delius's Requiem, completed in 1916 and dedicated to "the memory of all young Artists fallen in the war",; Paul Hindemith's When Lilacs Last in the Dooryard Bloom'd: A Requiem for Those We Love, commissioned in 1945 (premiered 1946) after the passing of Franklin Delano Roosevelt, and based on Walt Whitman's elegy written after the passing of Abraham Lincoln; and Dmitry Kabalevsky's Requiem (Op. 72; 1962), a setting of a poem written by Robert Rozhdestvensky especially for the composition. Herbert Howells's unaccompanied Requiem uses Psalm 23 ("The Lord is my shepherd"), Psalm 121 ("I will lift up mine eyes"), "Salvator mundi" ("O Saviour of the world," in English), "Requiem aeternam" (two different settings), and "I heard a voice from heaven." Some composers have written purely instrumental works bearing the title of requiem, as famously exemplified by Britten's Sinfonia da Requiem. Hans Werner Henze's Das Floß der Medusa, written in 1968 as a requiem for Che Guevara, is properly speaking an oratorio; Henze's Requiem is instrumental but retains the traditional Latin titles for the movements. Igor Stravinsky's Requiem Canticles mixes instrumental movements with segments of the "Introit," "Dies irae," "Pie Jesu" and "Libera me". Christopher Wood’s Requiem (premiered in 2012 under the direction of Paul Brough at St John's, Smith Square) was inspired by the public reaction to the death of Queen Elizabeth the Queen Mother, and returns to a more traditional form, setting virtually the complete Latin text from the Liber Usualis. In February 2013, an Arab Spring-inspired 'Requiem' by composer Rami Khalife was premiered by the Qatar Philharmonic Orchestra and The Leipzig Radio Choir, to great critical acclaim.
In the liturgical reforms of the mid-20th century in the Roman Catholic Church following the Second Vatican Council, there was a significant shift in the funeral rites used by the Church. The emphasis on sorrow and grief was to be replaced by one which also includes the whole community's worship of God and in which the deceased is entrusted to God's love, based on trust in the salvific value of the Passion, Death and Resurrection of Jesus Christ.
The term "Requiem Mass" was often replaced by the term Mass of the Resurrection or Mass of Christian Burial, although the former was never official terminology. In line with this shift, the use of black vestments was made optional (and had mostly disappeared by the late 20th century, at least in the United States, although their use is seeing a resurgence), with the preference of many being for white, the color of joy associated with Easter, or purple, for a muted version of mourning. The texts used for the service made a similar change, with the overall theme of the service to be a proclamation of the promise of eternal life made by Jesus.
A Solemn Requiem Mass is held by the Catholic Police Guild in October every year. It is celebrated in Westminster Cathedral, London to commemorate:
- Members of the Catholic Police Guild who have recently died
- Serving police officers and staff who have died or lost their lives in the course of their duty in the last year
- All deceased colleagues and friends in the police service.
Requiem in other rites and churches
Requiem is also used to describe any sacred composition that sets to music religious texts which would be appropriate at a funeral, or to describe such compositions for liturgies other than the Roman Catholic Mass. Among the earliest examples of this type are the German settings composed in the 17th century by Heinrich Schütz and Michael Praetorius, whose works are Lutheran adaptations of the Roman Catholic requiem, and which provided inspiration for the mighty German Requiem by Brahms.
Such works include:
- Greek Orthodox Church—Parastas
- Russian Orthodox Church—Panikhida
- Anglican (English) Requiem
Main article: Memorial service (Orthodox)
In the Eastern Orthodox and Greek-Catholic Churches, the requiem is the fullest form of memorial service (Greek: Parastas, Slavonic: Оpеlо). The normal memorial service is a greatly abbreviated form of Matins, but the Requiem contains all of the psalms, readings, and hymns normally found in the All-Night Vigil (which combines the Canonical Hours of Vespers, Matins and First Hour), providing a complete set of propers
for the departed. The full requiem will last around three and a half hours. In this format it more clearly represents the original concept of parastas, which means literally, "standing throughout (the night)." Often, there will be a Divine Liturgy celebrated the next morning with further propers for the departed.Because of their great length, a full Requiem is rarely served. However, at least in the Russian liturgical tradition, a Requiem will often be served on the eve before the Glorification (canonization) of a saint, in a special service known as the "Last Panikhida."

Anglicanism
The Anglican Book of Common Prayer contains no Requiem Mass, but instead a service named "The Order for the Burial of the Dead". Within this service are several texts with rubrics stating that they shall be said or sung by the priest or clerks. The first few of these texts are found at the beginning of the service, while the rest are meant to occur during the actual burial of the body into the grave. These texts are typically dividing into seven, and collectively known as "funeral sentences". Composers who have set the Anglican burial service to music include William Croft, Thomas Morley, Thomas Tomkins, Orlando Gibbons, and Henry Purcell. The text of these seven sentences, from the 1662 Book of Common Prayer, is as follows:
- I am the resurrection and the life, saith the Lord: he that believeth in me, though he were dead, yet shall he live: and whosoever liveth and believeth in me shall never die.
- I know that my Redeemer liveth, and that he shall stand at the latter day upon the earth. And though after my skin worms destroy this body, yet in my flesh shall I see God: whom I shall see for myself, and mine eyes shall behold, and not another.
- We brought nothing into this world, and it is certain we can carry nothing out. The Lord gave, and the Lord hath taken away; blessed be the Name of the Lord.
- Man that is born of a woman hath but a short time to live, and is full of misery. He cometh up, and is cut down, like a flower; he fleeth as it were a shadow, and never continueth in one stay.
- In the midst of life we are in death: of whom may we seek for succour, but of thee, O Lord, who for our sins art justly displeased? Yet, O Lord God most holy, O Lord most mighty, O holy and most merciful Saviour, deliver us not into the bitter pains of eternal death.
- Thou knowest, Lord, the secrets of our hearts; shut not thy merciful ears to our prayer; but spare us, Lord most holy, O God most mighty, O holy and merciful Saviour, thou most worthy judge eternal, suffer us not, at our last hour, for any pains of death, to fall from thee.
- I heard a voice from heaven, saying unto me, Write, From henceforth blessed are the dead which die in the Lord: even so saith the Spirit: for they rest from their labours.
 Music
Music
Main article: Music for the Requiem Mass
The Requiem Mass is notable for the large number of musical compositions that it has inspired, including settings by Mozart, Verdi, Brahms, Dvořák, Fauré, Duruflé,
and others. Originally, such compositions were meant to be performed in
liturgical service, with monophonic chant. Eventually the dramatic
character of the text began to appeal to composers to an extent that
they made the requiem a genre of its own, and the compositions of
composers such as Verdi are essentially concert pieces rather than
liturgical works.Many of the texts in the Requiem Mass have been set to music, including:
For many centuries the texts of the requiem were sung to Gregorian melodies. The Requiem by Johannes Ockeghem, written sometime in the later half of the 15th century, is the earliest surviving polyphonic setting. There was a setting by the elder composer Dufay, possibly earlier, which is now lost: Ockeghem's may have been modelled on it. Many early compositions reflect the varied texts that were in use in different liturgies around Europe before the Council of Trent standardised texts used in liturgies. The requiem of Brumel, circa 1500, is the first to include the Dies Iræ. In the early polyphonic settings of the Requiem, there is considerable textural contrast within the compositions themselves: simple chordal or fauxbourdon-like passages are contrasted with other sections of contrapuntal complexity, such as in the Offertory of Ockeghem's Requiem.
In the 16th century, more and more composers set the Requiem mass. In contrast to practice in setting the Mass Ordinary, many of these settings used a cantus-firmus technique, something which had become quite archaic by mid-century. In addition, these settings used less textural contrast than the early settings by Ockeghem and Brumel, although the vocal scoring was often richer, for example in the six-voice Requiem by Jean Richafort which he wrote for the death of Josquin des Prez. Other composers before 1550 include Pedro de Escobar, Antoine de Févin, Cristóbal Morales, and Pierre de La Rue; that by La Rue is probably the second oldest, after Ockeghem's.
Over 2,000 Requiem compositions have been composed to the present day. Typically the Renaissance settings, especially those not written on the Iberian Peninsula, may be performed a cappella (i.e. without necessary accompanying instrumental parts), whereas beginning around 1600 composers more often preferred to use instruments to accompany a choir, and also include vocal soloists. There is great variation between compositions in how much of liturgical text is set to music.
Most composers omit sections of the liturgical prescription, most frequently the Gradual and the Tract. Fauré omits the Dies iræ, while the very same text had often been set by French composers in previous centuries as a stand-alone work.
Sometimes composers divide an item of the liturgical text into two or more movements; because of the length of its text, the Dies iræ is the most frequently divided section of the text (as with Mozart, for instance). The Introit and Kyrie, being immediately adjacent in the actual Roman Catholic liturgy, are often composed as one movement.
Musico-thematic relationships among movements within a Requiem can be found as well.
 Requiem in concert
Requiem in concertBeginning in the 18th century and continuing through the 19th, many composers wrote what are effectively concert works, which by virtue of employing forces too large, or lasting such a considerable duration, prevent them being readily used in an ordinary funeral service; the requiems of Gossec, Berlioz, Verdi, and Dvořák are essentially dramatic concert oratorios. A counter-reaction to this tendency came from the Cecilian movement, which recommended restrained accompaniment for liturgical music, and frowned upon the use of operatic vocal soloists.
Notable compositions
Many composers have composed Requiems. Some of the most notable include the following (in chronological order):
- Ockeghem: Requiem, the earliest to survive, written sometime in the mid-to-late 15th century
- Victoria: Requiem of 1603, (part of a longer Office for the Dead)
- Mozart: Requiem in D minor, K. 626 (1791: Mozart died before its completion; Franz Xaver Süssmayr's completion is often used)
- Cherubini: Requiem in C minor (1815)
- Berlioz: Grande Messe des morts (1837)
- Brahms: A German Requiem, Op. 45, based on passages from Luther's Bible (1869)
- Verdi: Requiem (1874)
- Dvořák: Requiem, Op. 89 (1890)
- Fauré: Requiem in D minor, Op. 48 (1890)
- Duruflé: Requiem, Op. 9, based almost exclusively on the chants from the Graduale Romanum (1947)
- Britten: War Requiem, Op. 66, which incorporated poems by Wilfred Owen (1962)
- Stravinsky: Requiem Canticles (1966)
- Penderecki: Polish Requiem (1984, revised 1993 and 2005)
- Lloyd Webber: Requiem (1985)
- Rutter: Requiem, includes Psalm 130, Psalm 23 and words from the Book of Common Prayer (1985)
- See also: Category:Requiems
 Modern treatments
Modern treatmentsIn the 20th century the requiem evolved in several new directions. The genre of War Requiem is perhaps the most notable, which comprise compositions dedicated to the memory of people killed in wartime. These often include extra-liturgical poems of a pacifist or non-liturgical nature; for example, the War Requiem of Benjamin Britten juxtaposes the Latin text with the poetry of Wilfred Owen, Krzysztof Penderecki's Polish Requiem includes a traditional Polish hymn within the sequence, and Robert Steadman's Mass in Black intersperses environmental poetry and prophecies of Nostradamus. Holocaust Requiem may be regarded as a specific subset of this type. The Requiem Ebraico (Hebrew Requiem) (1945) by Austrian-American composer Eric Zeisl, a setting of Psalm 92 dedicated to the memory of the composer's father "and the other countless victims of the Jewish tragedy in Europe," is considered the first major work of Holocaust commemoration. John Foulds's A World Requiem was written in the aftermath of the First World War and initiated the Royal British Legion's annual festival of remembrance. Recent requiem works by Taiwanese composers Tyzen Hsiao and Ko Fan-long follow in this tradition, honouring victims of the 228 Incident and subsequent White Terror. Other recent requiems include "Ossetian Requiem" (2006), in memory of the victims of the Beslan tragedy, by Ivan Moody, the "Requiem In D-Minor" (2009) composed by Allan Loucks, and the Requiem by Man-Ching Donald Yu, in remembrance of the victims of the 2008 Sichuan earthquake.
Lastly, the 20th century saw the development of the secular Requiem, written for public performance without specific religious observance, such as Frederick Delius's Requiem, completed in 1916 and dedicated to "the memory of all young Artists fallen in the war",; Paul Hindemith's When Lilacs Last in the Dooryard Bloom'd: A Requiem for Those We Love, commissioned in 1945 (premiered 1946) after the passing of Franklin Delano Roosevelt, and based on Walt Whitman's elegy written after the passing of Abraham Lincoln; and Dmitry Kabalevsky's Requiem (Op. 72; 1962), a setting of a poem written by Robert Rozhdestvensky especially for the composition. Herbert Howells's unaccompanied Requiem uses Psalm 23 ("The Lord is my shepherd"), Psalm 121 ("I will lift up mine eyes"), "Salvator mundi" ("O Saviour of the world," in English), "Requiem aeternam" (two different settings), and "I heard a voice from heaven." Some composers have written purely instrumental works bearing the title of requiem, as famously exemplified by Britten's Sinfonia da Requiem. Hans Werner Henze's Das Floß der Medusa, written in 1968 as a requiem for Che Guevara, is properly speaking an oratorio; Henze's Requiem is instrumental but retains the traditional Latin titles for the movements. Igor Stravinsky's Requiem Canticles mixes instrumental movements with segments of the "Introit," "Dies irae," "Pie Jesu" and "Libera me". Christopher Wood’s Requiem (premiered in 2012 under the direction of Paul Brough at St John's, Smith Square) was inspired by the public reaction to the death of Queen Elizabeth the Queen Mother, and returns to a more traditional form, setting virtually the complete Latin text from the Liber Usualis. In February 2013, an Arab Spring-inspired 'Requiem' by composer Rami Khalife was premiered by the Qatar Philharmonic Orchestra and The Leipzig Radio Choir, to great critical acclaim.
Contents
1 Liturgical rite
1.1 Post Vatican II
1.2 Annual requiems
2 Requiem in other rites and churches
2.1 Eastern Christian rites
2.2 Anglicanism
3 Music
3.1 History of musical compositions
3.1.1 Requiem in concert
3.2 Notable compositions
3.3 Modern treatments
4 See also
5 Notes
6 External links
1 Liturgical rite
1.1 Post Vatican II
1.2 Annual requiems
2 Requiem in other rites and churches
2.1 Eastern Christian rites
2.2 Anglicanism
3 Music
3.1 History of musical compositions
3.1.1 Requiem in concert
3.2 Notable compositions
3.3 Modern treatments
4 See also
5 Notes
6 External links
Mozart: Requiem
Herbert von Karajan
👇 🎼 👇
👇 🎼 👇
Music for the Requiem Mass
🎼
Requiem (Mozart)
Requiem (Mozart)
Requiem on You Tube
https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=requiem&lclk=hd&filters=hd
🎼
https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=Requiem+